Today I woke up and took a look outside: the weather was so awful I decided to so something cool, at home. Today, I ported a Silverlight Windows Phone 7 game to WinRT in 9 hours. In this post, I share the “journal” I wrote will porting the app so that you can follow this process with many detail. I hope you will learn interesting stuff. Warning: the post is much longer than usual 🙂
Context:
- The original Windows Phone application is a Silverlight game called Touch’n’Match. This game is available in the marketplace for free. The goal is to select appropriate items from a board creating pairs or sequences. The fastest the player creates pairs, the more points he has.
- I’m not creating a common code base across the 2 platforms. I’m just “converting” the Silverlight version to WinRT.
- I’m not targeting a “ready to publish” version of the app today. I just want to be able to play the game on my //BUILD/ slate 🙂
Here is a quick video showing the game in action using the WP7 emulator:
[mediaplayer src=’/wp-content/uploads/Version_WP7.wmv’ ]
The video of the game running on the //BUILD/ slate is available at the end of this article 🙂
Tooling used:
- Windows 8 Consumer Preview
- Visual Studio 2011 Beta + Updates
- Visual Studio 2010 + SP1
- Windows Phone SDK 7.1.1 for Windows 8 support
- Resharper 7 EAP (I’m a big fan of R# and it’s going to be very helpful to map and adjust the namespaces…)
Now, let’s the hackaton begin 😀
9:50AM
The source code of Touch’N’Match is stored in SVN using Assembla. I’m performing a clean check out the trunk in my personal folder. I launch VS2010 to build the app and make sure the Windows Phone version works properly:
Everything seems ok. It’s time to launch VS11:
And to create a new project:
9:55AM
I’m going to start porting all the C# which is not linked to XAML. I expect to do that fairly quickly, the only thing I will have to rewrite (at least I think about at this time) is the part which deals with the isolated storage (API in SL for Windows Phone and WinRT are very different even though the principles are very similar).
I’m simply using drag’n’drop between the Windows Explorer and VS11 to add the files in the WinRT project.
I start with what I found the simple first, for example I start by porting the converters used in the XAML of the game. Because the interface has changed from:
public interface IValueConverter
{
object Convert(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture);
object ConvertBack(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture);
}
To:
public interface IValueConverter
{
object Convert(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, string language);
object ConvertBack(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, string language);
}
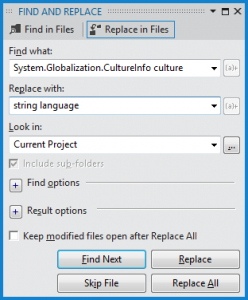
I’m simply doing a “Search and replace” to fix all those errors in one shot:
The Model folder contains just simple C# code, I have nothing special to do (which is nice!)
The Windows Phone version contains a class named ThemeService. This class was responsible for giving colors to use in the app based on the current accent color of the phone. In WinRT we don’t have the concept of accent colors. The app is supposed to ship with its own accent color. So I’m removing this part entirely for the moment.
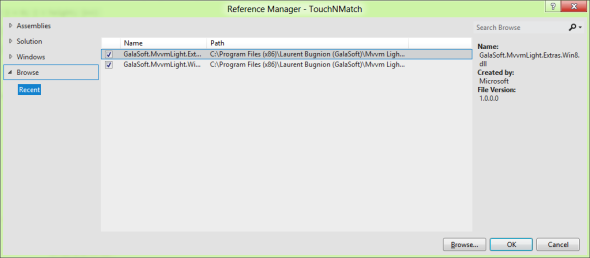
The ViewModel folder is linked to the MVVM Light framework. I already have the Windows 8 version installed on my machine, so I just have to reference the new assemblies:
Because I’m Resharper EAP for VS11 I can see very quickly the amount of errors when I open a file, using the indicators sitting next to the vertical scrollbars:
I’m now facing problems with the string resources. In the Silverlight version the app was localized the all the strings contained in .resx files. We were then able to access them using the types auto-generated and a binding in the XAML. This is no longer possible in WinRT. So the first thing I do is to create the new .resw files and put the strings there:
I then create a class to be able to access the string from C# (because the new .resw file does not generate static type automatically):
public static class AppResources
{
private static readonly ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
static AppResources()
{
resourceLoader = new ResourceLoader("PrototypeZero/AppResources");
}
public static string GetResources(string key)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(key))
throw new ArgumentNullException("key");
return resourceLoader.GetString(key);
}
}
I don’t know if the handling of .resw is going to change or not with the final version of VS11. If it does not I think it could be a good idea to use T4 templates to automatically generates the static types (that would make the porting much easier). But this is out of the scope of this post 🙂
I know have to change all the AppResources.Key to AppResources.GetString(Key)…
I then encountered an error with a call to ToShortDateTimeString() on a DateTime object. I replaced this call with ToString(“d”) which is supposed to do the same thing. It looks like all formatting and parsing of DateTime structure is now handle by the DateTimeFormatter class.
10:35AM
Conversion of the following folders is completed:
- Converters
- Model
- Services
- ViewModel
I’m now going to deal with the isolated storage… The API used in the Silverlight app was very simple:
public class IsolatedStorageHelper
{
T Load(string name) where T : class, new();
void Save(string name, T instance);
void Delete(string name);
}
The conversion was not very complicated. All synchronous methods became asynchronous and I use the new API available in WinRT. One noticeable thing is the fact that we don’t have a File.Exists() API, so I ended up writing the following helper method:
private async static Task GetFile(string name)
{
var folder = ApplicationData.Current.LocalFolder;
try
{
return await folder.GetFileAsync(name);
}
catch (FileNotFoundException)
{
return null;
}
}
And the final API in the WinRT project:
public class IsolateStorageHelper
{
async Task Load(string name) where T : class, new();
async void Save(string name, T objectToSave);
async void Delete(string name);
}
Notice that now, all the methods are asynchronous…
10:50AM
All the code ported in the WinRT project now builds with success. Let’s bring more code in the WinRT project…
I found out that the Storyboard.SetTargetProperty API has changed:
Silverlight version: Storyboard.SetTargetProperty(Timeline, PropertyPath)
WinRT version: Storyboard.SetTargetProperty(Timeline, string)
Also, the EasingFunction property of the DoubleAnimation type has changed from IEasingFunction (Silverlight) to EasingFunctionBase (WinRT).
Finally the GeneralTransform.Transform(Point) API has changed to GeneralTransform.TransformPoint(Point)
11:00AM
It looks like it’s now time to bring some XAML 😉
The home page of the WP7 version was using a pivot control. I don’t need a pivot and I can display everything on the screen at once. So I’m just replacing the PivotControl with a grid of 3 columns.
The issue I faced while moving the first XAML code was due do localization. In the Silverlight version we used a very common localization approach using a binding to a static resource:
It looks like it’s not that easy to do that in WinRT… I looked up on the Internet and found this post. Because I’m lucky, Tim Heuer a Program Manager on the XAML team replied 3 days ago to explain how localization now works in XAML WinRT apps. Here is how it works (full documentation available here):
- Assign a x:Uid to the XAML element you want to localize (for example x:Uid=”buttonOnePlayer”)
- Create a resource in the resw file with a key buttonOnePlayer.Content (because we want to set the Content property of the button)
- The resource will be automatically take at runtime
I think I like this approach even though it is too early to come with a conclusion. I would like to have more tooling to pick the resources from the resw right from the XAML editor…
The other thing I must deal with is the fact that the Silverlight version was using multiple behaviors:
This is not available out of the box in WinRT. I found a post describing an approach the port the Silverlight code to WinRT but I didn’t wanted to try it today. So my approach is to find a way to remove each those behaviors…
The Silverlight game was created with the Windows Phone 7.0 SDK, based on Silverlight 3. At this time there was no Command property available on a Button. This is no longer the case and of course neither the case in WinRT. So I can already fix a lot of them.
The other usages of behaviors are trickier and I will see how I fix them later…
A TriggerAction NavigateToPageAction was used to nagivate from page to page right from the XAML. In order to enable navigation from my ViewModel classes, I created a NavigationService class:
public static class NavigationService
{
private static Frame rootFrame;
public static void Initialize(Frame frame)
{
rootFrame = frame;
}
public static bool Navigate(object parameter = null)
{
var type = typeof(T);
return Navigate(type, parameter);
}
public static bool Navigate(Type source, object parameter = null)
{
return rootFrame.Navigate(source, parameter);
}
}
Of course this class should be hidden behind an interface to improve testability of ViewModel classes, but again, this is out of the scope of this article…
12:05PM
It’s time to take a look at the most complex page of the app…
The first step was to port the Resources section where converters and storyboard were defined. It was simply a copy-paste from VS2010 to VS11 🙂
Then I copy-paste the content of the page, and started to fix problems:
- I updated the localization using the techniques I described before
- I commented (temporarily of course) the use of Triggers and Actions
- I added a resource dictionary which was missing from the VS11 solution
- I updated the resource usage, the Silverlight version had reference to phone-specific resources (like PhoneBackgroundBrush…)
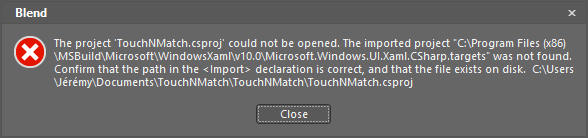
I fired Blend in order to find out the new resources available. Unfortunately for me I started by an error message when I wanted to create a new WinRT project or opened an existing one:
I looked up on the Internet but I cannot find the source of this issue. The most interesting thread is this one on MSDN forums… but it does not fix my issue.
So I ended up creating a new folder in the C:\Program Files (x86)\MSBuild\Microsoft\WindowsXaml by copying the V11.0 folder… It was enough to have Blend working like a charm:
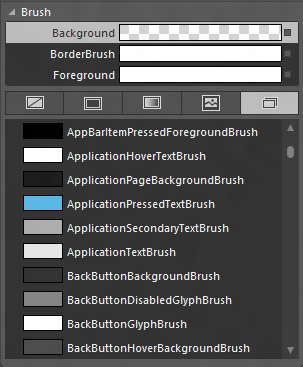
And I can see what resources are available in WinRT:
The next step is to use the Find & Replace dialog to fix all the old references… Here is the mapping I used:
| Silverlight for Windows Phone | XAML WinRT |
| PhoneForegroundBrush | AppBarItemForegroundBrush |
| PhoneBackgroundBrush | ApplicationPageBackgroundBrush |
| PhoneContrastBackgroundBrush | ApplicationHoverTextBrush |
| PhoneDisabledBrush | ControlDisabledBrush |
| PhoneHorizontalMargin | 12,0 |
| PhoneVerticalMargin | 0,12 |
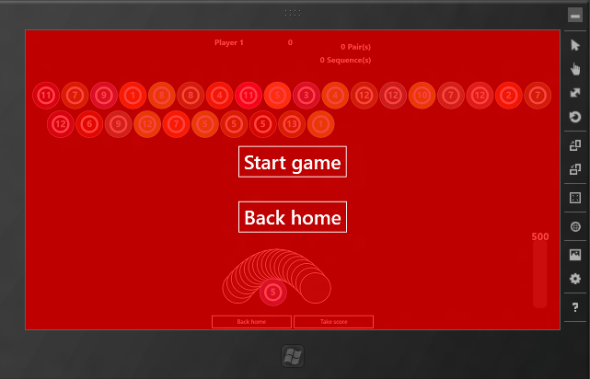
1:00PM
I finally have something which can be launched (sorry for the ugly red background, I was just testing resource picking :p):
It’s time to take a break 🙂
2:30PM
I’m back. Even though I was able to launch the app before the break it was not yet functional… I commented a lot of things in the XAML just to make it build. In particular, I know must solve the an issue with sound playback: the WP7 was using an TriggerAction to play a sound. This TriggerAction was used directly in the XAML to play sound when a button was click for example.
3:30PM
I just spent about 1 hour trying to play sound in the app but I cannot get it working! I can play sound if I instantiate a MediaElement in the XAML, but if the MediaElement is instantiated in code, it doesn’t work. Because this issue is driving me crazy, I’m just assuming the version of today will be without sound 😀
4:00PM
Another use of the behavior in the WP7 version: switch the current state of a control based on the value of an enum. I’m replacing the behavior with some code:
- I created a custom control which has the enumeration as a dependency property
- This dependency property is bound to the enumeration defined in the ViewModel
- This dependency property has a PropertyChangedHandler callback defined to be notified each time its value change
- When the value of the enum change, I manually update the current state (VisualStateManager.GoToState)
5:00PM
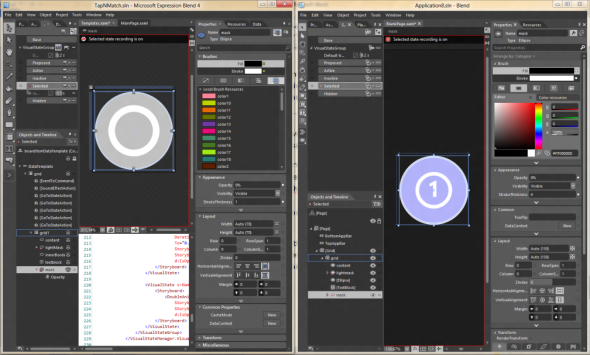
The idea is described previously is supposed to work… but it doesn’t!
So after spending 30minutes trying to figure out why the animation between the states wasn’t working (+ other strange UI issues) I decided to recreate the template in Blend. It took me about 5minutes using Blend 4 for the original WP7 version and Blend 5 for the new WinRT version side by side:
I now have to fix another issue: the WP7 hardcoded the layout of each item on the board (the number of columns and row was fix). I’m going to update that to be more flexible…
6:30PM
The hardcoded stuff was more complicated than expected but it’s now working… It was mainly due to the fact that we hardcoded the number of columns and rows in the WP7 version. Now because the resolution of the screen can change, I have to compute how many items fit on the board…
Another control was still missing and was used to display the scores. I create a new UserControl in VS11 and copy/paste the XAML from VS2010. I must do the usual work:
- Update the resource to have the appropriate mapping in the .resw file
- Adjust namespace
- Remove behavior and replace with standard Command
- Remove sound effects
7:15PM
At this point, only one minor issue is still bothering me, and I’m starting to get tired… When the app there was a DoubleAnimation animating the FontSize property of a TextBlock element. This does not work in WinRT… Because I don’t want to waste time finding out, I’m just using instead a ScaleTransform to achieve the same effect 🙂
7:35PM
I think it’s all for today. I can now launch the app and play the game it was my original objective !
Here is a video showing me playing the game:
[mediaplayer src=’/wp-content/uploads/Version_WinRT.wmv’ ]
Conclusion
First of all, I’m kind of happy I finally had the occasion to jump into the WinRT world. Porting this app was a very interesting experience even though I must admit I was kind of angry sometimes!
Because I’m very familiar with XAML and C# it was easy to get into the WinRT world. Here is a summary of the main changes I made today between the 2 versions:
- Adjust namespaces
- Rewrite the isolate storage layer
- Remove any dependency toward behaviors (TriggerAction / Behavior<T>…)
- Rewrite a part of the game engine because the WP7 version hardcoded the number of items on the board
I was able to reuse most of the XAML, but I think this is true because the app was a game. I have another app I’m thinking to port in WinRT and I think it will need a major rewrite of its UI to leverage the size of the screen.
I hope your learnt interesting things in this post. Feel free to let a comment if you have any specific question.